Vauxhall Gardens: A History
David Coke & Alan Borg
The Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens is one of the places I’d love to slip back in time to visit, just to catch a glimpse of what it was like. After recently splurging to buy this lovely coffee-table book, I thought it might make a wonderful subject for a new blog series. But do buy the book too, if you can! The photos are fabulous!
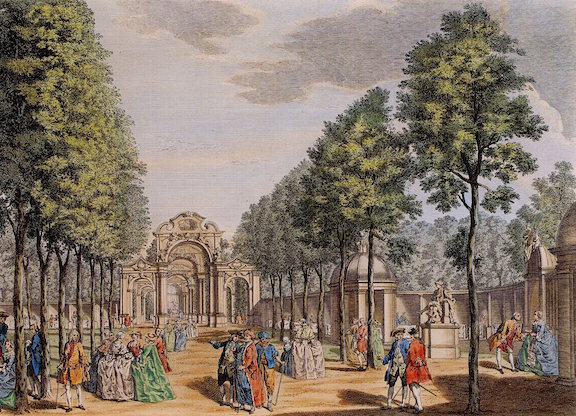
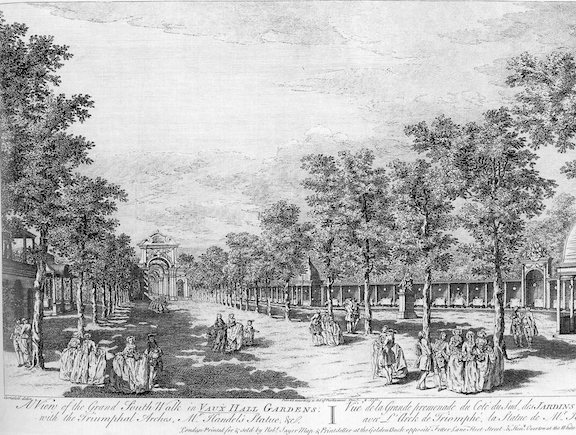
A Statue for the Greatest Composer of English Music (1738)
The life-sized sculpture of George Frideric Handel by Louis François Roubiliac (1702-62) was
the most important of Tyers’s early series of artistic commissions for the gardens. This work epitomised the explosive moment of the English Rococo style, not for any inclusion of outwardly Rococo motifs, but for the new spirit of playfulness and informality that it embodied, and it came to personify Vauxhall Gardens.
There is now near finished a Statue of the justly celebrated Mr. Handel, exquisitely done by the ingenious Mr. Raubillac, of St. Martin’s-Lane, Statuary, out of one entire Block of white Marble, which is to be placed in a grand Nich, erected on Purpose in the great Grove at Vaux-hall Gardens.
The “Grand Nich” or “Grand Alcove” was demolished after a decade to make room for more supper-boxes, and the statue was left free-standing until 1762, when it was arranged under a Doric portico similar in size to the “Grand Nich.” In 1786, following the Vauxhall Jubilee celebrations, it was removed to the back of the Orchestra. Before it was removed from the gardens in 1818, it held court in the New Supper Room built in 1791, and then, in 1813, “to its own small circular domed temple behind the Orchestra.”
Victoria and Albert Museum
The Handel statue can be seen today at the Victoria and Albert Museum in London, along with a group of the original supper-box paintings and Roubiliac’s terracotta model for the portrait bust of Jonathan Tyers.
In spite of many years’ exposure to the elements, to vandalism, accidental damage, relocations and restorations, the surface of the sculpture still bears the sculptor’s marks and finished, evidence of his high degree of skill and craftsmanship, equally of his mastery and love of the material.
“A mass audience for contemporary art”
Artwork was an important element in Jonathan Tyers’ vision of capturing his visitors’ emotions and induce them “to enjoy themselves, to refresh their spirits and to spend their money.” In order to do this, Tyers formed an alliance with his friend William Hogarth’s nearby academy to produce the work he needed, which included buildings, paintings, sculptures, furnitures, tableware, glass, interiors, and lighting. This arrangement benefitted both parties, providing Tyers with the high-quality artisans he needed at a reasonable cost, and an opportunity for Hogarth’s students’ work to be displayed to the public in a way not seen before. The person chosen to manage the project was the theatrical scene-painter, Francis Hayman (1708-76).

Francis Hayman and studio, The Milkmaids’ Garland, oil on canvas, c. 1740 (Victoria and Albert Museum, London)
The Supper-Box Paintings
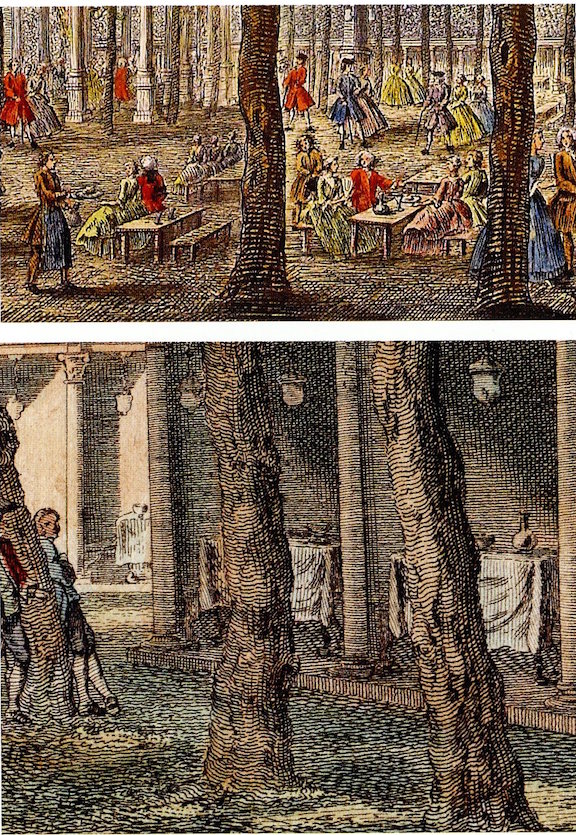
To add color and enhance the visitor’s mood, the back upper wall of each supper-box in the 1730’s and 40’s was decorated by an eight foot by five painting, designed by Francis Hayman and H.F. Gravelot and painted by the students at St. Martin’s Lane Academy. These paintings
represent people from all sectors of society, from villagers, peasant children and milkmaids to aristocratic and fashionable ladies and gentlemen. Painted on a large scale, some of the figures are nearly life-sized and close enough to the picture plane for the viewer to discern their expressions and interrelationships.

Francis Hayman and stuido, Country Dancers round the Maypole, oil on canvas, late 1730’s (Victoria and Albert Museum, London)
The pictures depicted scenes of theatre, daily life and rustic amusements. A Toupee letter (see post here) of 28 June 1739 states that, when the paintings were revealed,
the eye is relieved by the agreeable surprise of some of the most favoured fancies of our poets in the most remarkable scenes of our comedies, some of the celebrated dancers, &c. in their most remarkable attitudes, several of the childish diversions, and other whims that are well enough liked by most people at a time they are disposed to smile, and every thing of a light kind, and tending to unbend the thoughts, has an effect desired before it is felt.
The Display of the Paintings
In the 1730’s the supper-boxes were open on all sides during daylight hours, to allow visitors to enjoy the views over the neighbouring countryside. However, as dusk fell, Tyers had created two extraordinary surprises for his guests. The first was the almost magical instantaneous illumination of the gardens with oil lamps. This wonder was swiftly followed by a second spectacular special effect, namely:
a master piece of machinery, by which all the English ladys and delicate gentlemen are in a moment screend from the damps of the night air. […] When the clock strikes nine, there is heard a third sound of the whistle, and immediately there rises, as out of the earth, a vast number of rollers, which unfolding themselves as they rise, cover all the boxes in three of their sides, and fasten themselves in the extremitys of each box. All these coverings are painted with elegant designs, in lively colours, so that each box is enclosed by three large pictures, and at the same time that they completely protect the company from the injurys of the air, present a numerous collection of grand and pleasing paintings.
By 1741, all the paintings were fixed in position on the back or side wall of the boxes… Tyers had introduced further improvements and the supper-boxes had been adapted to make them more weatherproof, more robust and more firmly divided from each other.

Francis Hayman and studio, Bird-catching, by a Decoy with a Whistle and Net, oil on canvas, c. 1740 (Victoria and Albert Museum, London)
In spite of all the damage inflicted on these paintings by their exposure to the weather, the proximity of food, wine, candles, and oil lamps—not to mention the early days of being rolled up and down on a nightly basis—many of these paintings remained at Vauxhall for a hundred years.
Susana’s Vauxhall Blog Post Series
- Vauxhall Gardens: A History
- Vauxhall Gardens: Jonathan Tyers—“The Master Builder of Delight”
- Vauxhall Gardens: A New Direction
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Orchestra and the Supper-Boxes
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Organ, the Turkish Tent, and the Rotunda
- Vauxhall Gardens: Three Piazzas of Supper-Boxes
- Vauxhall Gardens: “whither every body must go or appear a sort of Monster in polite Company”
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Competition
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Artwork, Part I
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Artwork, Part II
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Music, 1732-1859
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Business Side
- Vauxhall Gardens: Developments from 1751-1786
- Vauxhall Gardens: Thomas Rowlandson’s Painting (1785)
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Third Generation of the Tyers Family and the Jubilee of 1786
- Vauxhall Gardens: An Era of Change (1786-1822), Part I
- Vauxhall Gardens: An Era of Change (1786-1822), Part II
- Vauxhall Gardens: An Era of Change (1786-1822), Part III
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part I
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part II
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part III
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part IV
- Vauxhall Gardens: Farewell, for ever