Amusements of Old London
William B. Boulton, 1901
“… an attempt to survey the amusements of Londoners during a period which began… with the Restoration of King Charles the Second and ended with the accession of Her Majesty Queen Victoria.”
“Modern” folks less brutal and more sophisticated
People of condition in the reigns of Anne and the Georges flocked to the Strand or to Covent Garden to see waxworks at Mrs. Salmon’s, or puppet-shows at Mr. Powell’s, or to watch Mrs. Saraband’s dogs and monkeys going through the operations of a siege with toy cannons and scaling-ladders.
Side by side with these innocent simplicities flourished the brutalities which we have examined in our inquiries into the humours of Hockley, the cockpit and the prize-ring, the last two at least of which famous institutions depended upon the support of well-to-do people for their prosperity and development. So too with the great mass of the people, separated in those days much more sharply from the classes than to-day. They delighted, as we have seen, in the primitive joys of Bartholomew’s Fair or the tea gardens, and were always ready to see much fun in the spectacle of a man grinning through a horse-collar. From such innocent diversion they would turn with joy to the horrors of the duck hunt or the cockshy; and a good place of vantage from which to see old Lovat’s head roll on the scaffold at the Tower, or Jack Rann swing into the air at Tyburn Tree, was held worth while spending the previous day to secure.
Whatever else may be said of the modern entertainments which appeal to the tastes and the purses of the London of to-day, it will not be contended that they lack humanity or err on the side of simplicity in execution or design.
“Simple and curious entertainments”
The naïveté of the audiences of the early part of the last century, and the ease with which they were amused, appear very plainly, we think, in the success which rewarded some very simple and curious entertainments of a spectacular character, which, by reason of that success, became serious competitors of the legitimate drama at Drury Lane.
Puppet Shows
Great people flocked to Mr. Powell’s establishment under the Piazza in Covent Garden in numbers which seriously reduced the takings of the patent houses, and hampered the progress of the exotic opera, then lately introduced into England.
These included marionette plays mixing biblical stories with Punch and Judy characters, such as “Punch and Judy dancing in Noah’s ark, Punch subsequently seating himself on the Queen of Sheba’s lap, fighting the Duke of Lorraine, and selling the King of Spain a bargain.”
Mrs. Salmon’s waxworks in Fleet Street near Temple Bar, foreshadowed Madame Tussaud’s.
M. Bisset astonished the town… with his Cats’ Opera and troupe of other animals; monkeys taking wine together, riding on horses, and dancing minuets with dogs. One of M. Bisset’s hares walked on its hind legs and beat a drum… [He] also induced his six turkeys to walk through the steps of a country dance.
Pantomime, like Opera, crept into England at the beginning of the eighteenth century, “comique masques in the high style of Italie” were announced, and a ballet at Drury Lane of the Loves of Mars and Venus, where the whole story was told by gesture… foreshadowed the real pantomime which soon followed. Rich at Lincoln’s Inn Theatre produced a piece called “Harlequin Executed” in 1717, which is accepted as the first real pantomime by historians of the stage… Even Garrick himself found the pantomime a serious rival, and was wont to reproach his audiences in the prologues and epilogues which he turned so neatly.
In the “modern” Victorian era, Boulton cites the “silly performances of the medical mountebank. Katerfelto
…took advantage of an epidemic of influenza to work upon the nerves of audiences with magic langterns and fearsome images of microbes and animalculae. His darkened rooms, black cats, and electric machines impressed his visitors hugely, instead of anticipating the fairly obvious fact later established by a magistrate, when his fire balloons set haystacks alight, that he was a rogue and a vagabond.
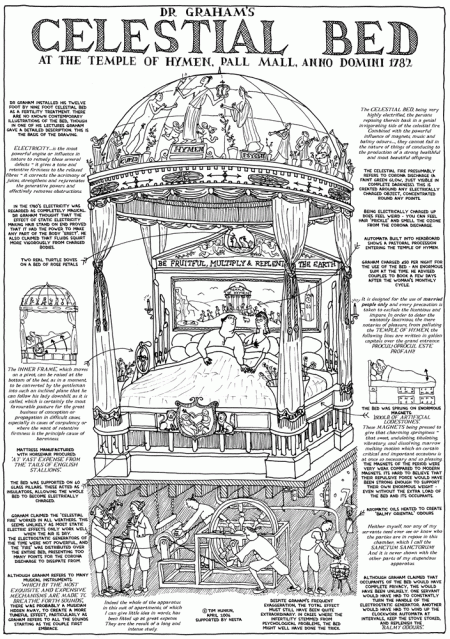
Dr. Graham, with the help of the lovely Emma, advocated mud-baths and lectured on “perpetual youth and beauty,” with the illustration of “blooming nursemaid… as the ‘Goddess of Health.'” The Celestial Bed held “great attractions for those wanting heirs, the ‘rosy Goddess of Health assisting at the celestial matters… and that sacred Vital Fire over which she watches.’ “With such attractions as these, Dr. Graham contrived to fill his rooms with a mob of silly people at five shillings a head.”
Philip Astley of Astley’s Amphitheatre was a “true pioneer” in the equestrian entertainment business “and should be canonised as the patron saint of all ringmasters. Astley saved George III’s life on Westminster Bridge and received a royal license. See more about Astley’s Amphitheatre in a previous post.
Like Heidegger, Tyers and others, Philip Astley and his son “claim mention here as men whose fortunes were made by devoting their energies to the amusement of the London of their day.”
Then there was cudgel-playing at open spaces like Spa Fields that drew large crowds. In 1768, “an extraordinary battle was fought in the Spa Fields by two women against two taylors for a guinea a head, which was won by the ladies, who beast the taylors in a severe manor.”
 At Spa Fields and other places, grinning matches were popular attractions. In 1779, the authorities took advantage of “such assemblies of British manhood” by offering “an ox roasted whole and unlimited beer to the “friends of their king and country,” hinting at the advantages of enlistment. “Some men were enlisted, but more were impressed, as the bloodhounds were on the scent, and ran breast high.”
At Spa Fields and other places, grinning matches were popular attractions. In 1779, the authorities took advantage of “such assemblies of British manhood” by offering “an ox roasted whole and unlimited beer to the “friends of their king and country,” hinting at the advantages of enlistment. “Some men were enlisted, but more were impressed, as the bloodhounds were on the scent, and ran breast high.”
Boulton feels that Londoners came late to appreciate the value of the Thames as a source of entertainment, although its value for transportation exceeded London roads as late as the Regency.
People did swim in the Thames from Stuart times to George IV, however. “Mr. Benjamin Franklin, has left record of a swim which he took through London from Lambeth to London Bridge in the reign of George the Third.” In 1807, Lord Byron swam from Lambeth three miles with the tide.
The Thames appears to have been used as an opportunity for the common people to express their views without fear of retribution. People of fashion who traveled to Vauxhall by boat would hire musicians, not just for the entertainment value, but also for protection from unruly hecklers. “It was the pride and joy of the average boatload of apprentices from the city to unite the vulgarity of their whole company in an epithet of suitable brevity, and fire it off upon every passing boatload of their betters they encountered on the voyage.
The Folly, the only floating place of entertainment of which there is record, a large hulk moored off Somerset House in the days of the Restoration, and fitted up as a musical summer-house for the entertainment of the quality, sank from a resort of the fashionables “to a receptacle for companies of loose and disorderly people for the purposes of drinking and promiscuous dancing.”
The Ranelagh Regatta of 1775 was the first of many such functions. Later on, the proprietors of Vauxhall Gardens began offering prizes for sailing races, and that spurred on more interest in leisure sailing on the Thames.

Vauxhall Sailing Match, engraving, 1800 (Minet Library, London, Lambeth Archives Department, V. fo. 57). This appears to be the only surviving image of one of the Vauxhall sailing matches.
Then there was the cock-shy, or cock-throwing, which was celebrated on Shrove Tuesday.
On that holy day you might see, in all open parts of the town, cocks or hens tied by the leg, their owners offering sticks at twopence a throw at a range of a chain, or twenty-two yards, just, in fact, as one used to throw at cocoa-nuts at a country fair. The cock had a certain length of strong in which to manoeuvre, and his master had trained him to avoid the knock over, which him the property of his assailant, as long as possible, and so to earn may twopences.
The duck hunt, however, was not limited to a season.
The duck-pond was a small affair, and boarded to the height of the knee round its edges to prevent the excited spectators from falling in in their eagerness to follow the incidents of the sport. These all arose from the movements of a pinioned duck which was put into the water and hunted by a spaniel or spaniels. “It escaped,” we are told, “as long as it was able by diving.”
Survival of the Fittest
Of the amusements of our ancestors in London which we have examined in our inquiry, how many have survived to our times. Practically one, and one only, the theatre, which to-day perhaps fills a greater place than ever amongst the diversions of the town… Parks, of course, remain, but they are no longer the playground of fashion which London made of them in the days of the Ring or the Mall. The tea gardens and Vauxhall were features of the London of other days, which all who have studied their old delights must regret… We may congratulate ourselves upon the change in taste and manners which has rendered the excsses of the play tables impossible in these days. No one regrets the disappearance of Hockley in the Hole, or the closing of cockpits and prize-rings… Speaking generally, Londoners of all ranks have exchanged most of their former joys for diversions in which bodily exercise takes a chief part; the man who formerly lost his fortune at hazard or faro at White’s or Brooks’s now spends it in healthy forms of sport which take him over the country, and indeed, over the globe for its gratification. Men of a lower station play cricket and football or ride bicycles when they are young, and look on at others doing the same when age overtakes them. And London and England have surely gained by the change.