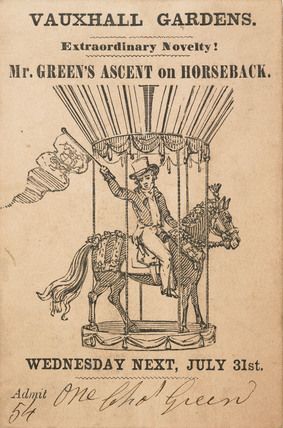
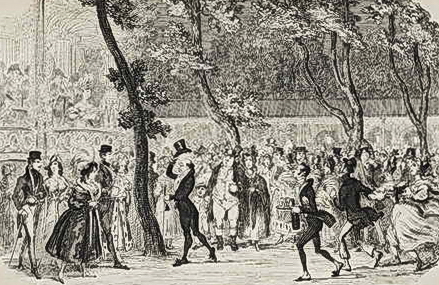The Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens is one of the places I’d love to slip back in time to visit, just to catch a glimpse of what it was like. After recently splurging to buy this lovely coffee-table book, I thought it might make a wonderful subject for a new blog series. But do buy the book too, if you can! The photos are fabulous!
The Final Season: 18-25 July, 1859
The Public is respectfully informed that this celebrated Place of Amusement, after an existence of nearly a Century and a Half, and receiving within its Portals the elite of the World is DOOMED TO BE DESTROYED; on Tuesday 26th Workmen will commence taking down the whole of the Buildings, and clearing the Ground in order to Let it for Building purposes. It is therefore with great pleasure that Mr G Stevens, for thirty five years connected with the establishment, informs the public that, through the kindness of the owner of the property, he is enabled to open the Gardens for The last Illuminations! The last Concerts! The Last Horsemanship! The Last Fireworks! The Last Music! The last Dancing! The Last Suppers! And The Last Punch!
On the last night, the “Grand Illumination Gala” included a military band in the Old Orchestra, a juvenile ballet; an equestrian troupe in the Rotunda, as well as numerous acrobats and rope dancers. Dancing on the new Leviathan platform ended with the usual fireworks, but no balloons.
The doors opened at 7 p.m., admission was only 1s, and over fifteen thousand people attended. At the end of the evening Mr. Russell Grover sang the last song, Nevermore shall I return; the last dance was a gallop and, after a short period of silence, the National Anthem was played. Then people began running to the trees on the platform breaking off twigs as souvenirs. Arthur Munby was there and recorded in his diary:
To Vauxhall. It was the last night: dense crowds of people filled the gardens: the circus, the ballet, the dancing & concerts, the supper-rooms, the rifle shooting, the fortune telling, the colored maps and the statues in the long walks—all were there as usual; there was no sign of dissolution: there was nothing in the noisy gaiety of the people (except perhaps that noisy gaiety itself) to show that they knew they were meeting there for the last time. But over all, in large letters formed of colored lamps, hung the words ‘Farewell for ever.’ These were the moral of it all… It is indeed much for a thoughtful man, to have seen the last of Vauxhall: to muse for the last time in those dim lighted alleys, and cry Vanitas vanitatum, and call up melancholy shows of Kings & Court ladies to put to shame the living laughing crowd: but the real sting is, that it is all over.
It’s all gone
All moveable items were sold at auction at bargain prices. The property itself, which was by now extremely valuable for development, was divided up into building plots. The only building left standing today—and it is nearly unrecognizable at this point—is the house that was originally built for the widow of Jonathan Tyers the younger.

Anon., The Pavilion and Colonnade, Vauxhall Gardens, watercolour, November 1859 (Houghton Library, Cambridge, Mass., Harvard Theatre Collection, Evert Jansen Wendell Bequest, TS 943.6.8F). The pictures have been removed from the walls and workmen prepare for the final demolition.
Why did Vauxhall close?
The weather was always a problem, and became a standing joke that farmers could always count on rain on the day of Vauxhall’s opening for the season. As the years passed, however, “an increasing number of covered areas, where entertainment could be provided even in a downpour” were introduced. Inclement weather is nothing new to outdoor events, but generally “if the attraction is good enough, the public will put up with the rain and the inconvenient delays or postponements associated with bad weather.”
Essentially, though, the Gardens failed to appeal to the Victorian middle classes.
In the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries visitors to Vauxhall would experience an idealized version of a rural idyll—trees, walks and nightingales, supplemented increasingly by music, dining, drinking and man-made illusions… By the end of the eighteenth century, however, it was not enough; the changes in the structure of London society… brought to the gardens a new, less sophisticated clientele for whom the rural idyll no longer exerted its traditional charm. Londoners increasingly saw themselves as citizens of a great industrial power that was coming to dominate the world through trade and military might… [T]he new audiences wanted to be entertained, amazed and thrilled by new attractions that appealed to the self-confident and patriotic spirit of the age.
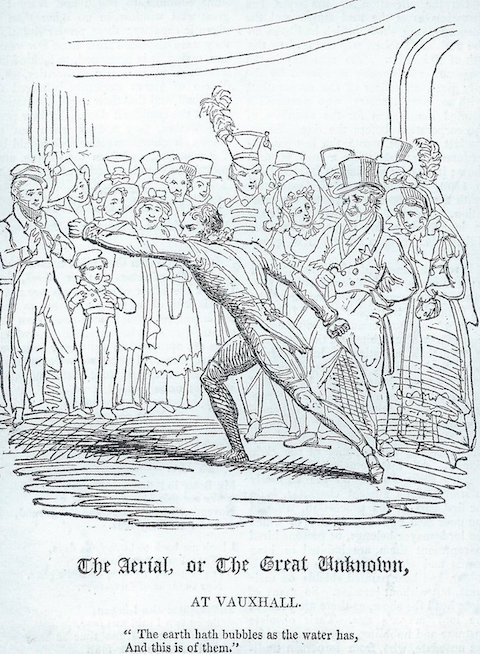
Madame Saqui’s daring high wire act and Charles Green’s balloons kept the place running long past the time it would naturally have folded. Expensive new novelties added rarely paid for themselves. Inept management and annual battles with magistrates over the renewal of the license—which resulted in increasing restrictions—also contributed to Vauxhall’s demise.
“There was, of course, always a significant section of the potential Vauxhall audience who opposed all attempts to turn the gardens into a modern popular attraction and pined for the good old days under Tyers.” However, in its beginnings, the Vauxhall area was largely rural. “The creeping urbanisation of the area brought with it the seeds of the final failure of the gardens. As they were no longer truly rural, the original reason for their existence disappeared. Yet if they were to offer little more than the theatres and music halls, they were a long way from the centre of town.”

Vauxhall Gardens, photograph, c.1859 (Lambeth Landmark, 1259). One of only two known nineteenth-century photographs of the gardens. Lit by the setting sun, the figures in the foreground are standing on the New Monster (or Leviathan) Platform and give an idea of the scale of the Orchestra, the original building of 1758 much altered and lamp-encrusted. The caryatids supporting the sounding board were probably added during the remodeling of 1845.
Vauxhall, farewell forever
Susana’s Vauxhall Blog Post Series
- Vauxhall Gardens: A History
- Vauxhall Gardens: Jonathan Tyers—“The Master Builder of Delight”
- Vauxhall Gardens: A New Direction
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Orchestra and the Supper-Boxes
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Organ, the Turkish Tent, and the Rotunda
- Vauxhall Gardens: Three Piazzas of Supper-Boxes
- Vauxhall Gardens: “whither every body must go or appear a sort of Monster in polite Company”
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Competition
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Artwork, Part I
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Artwork, Part II
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Music, 1732-1859
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Business Side
- Vauxhall Gardens: Developments from 1751-1786
- Vauxhall Gardens: Thomas Rowlandson’s Painting (1785)
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Third Generation of the Tyers Family and the Jubilee of 1786
- Vauxhall Gardens: An Era of Change (1786-1822), Part I
- Vauxhall Gardens: An Era of Change (1786-1822), Part II
- Vauxhall Gardens: An Era of Change (1786-1822), Part III
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part I
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part II
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part III
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part IV
- Vauxhall Gardens: Farewell, for ever