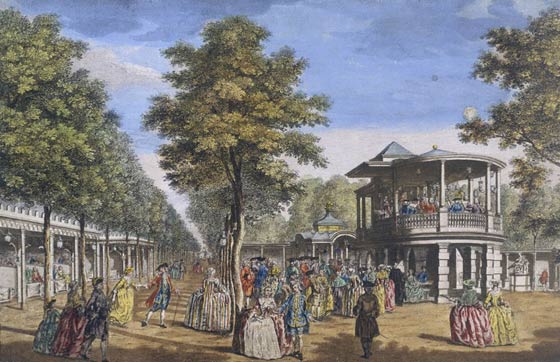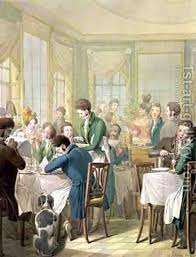Researching the Palais Royal
One of the fun things about writing—for me, at least—is the research. I love to dig into history; in particular, I love to look for just the right setting to help a scene come alive. Lady Chance, the follow-up book to Lady Scandal, comes out this August; it’s set in Paris of 1814, and since gambling and cards are in the book, that meant I could use the Palais Royal.
The palace was originally designed by Jacques Lemercier and construction started 1628 for the infamous Cardinal Richelieu. It was originally known as the Palais Cardinal, but became a royal palace after the cardinal bequeathed the building to Louis XIII.
Louis handed the palace to the Queen Mother, Anne of Austria, and then Henrietta Maria and her daughter Henrietta Anne Stuart, who had escaped from the English civil war, took up residence. Henrietta Anne later married Phillipe de France, duc d’Orléans, and the palace became known as the House of Orléans. The duchesse was the one who created the ornamental garden of the palace.
Louis XIV was succeeded by his great-grandson, and the duc d’Orléans became regent of young Louis XV. The Palais Royal was then opened so the public could view the Orléans art collection, and that began the palace’s more public life.
Louis Philippe II held the royal palace from 1780 until his death. He renovated the building, and the garden was now surrounded by a mall of shops, cafes, salons, refreshment stands and bookstores.
At that time, the Palais Royal became a meeting ground for revolutionaries. Its owner, Philippe d’Orléans sided with the revolutionaries. He changed his name to Philippe Égalité and his house became the Palais de l’Égalité. He opened the gardens to the public and enclosed them with colonnades lined with shops.

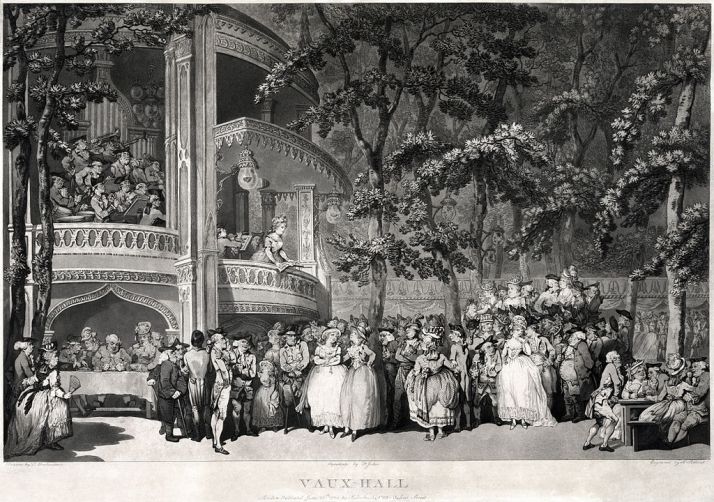
On the ground floor shops sold “perfume, musical instruments, toys, eyeglasses, candy, gloves, and dozens of other goods. Artists painted portraits, and small stands offered waffles.” The demi-monde could also parade their wares—themselves—and often had rooms on the upper floors for their customers’ convenience.
By 1807, the Palais Royal boasted “twenty-four jewelers, twenty shops of luxury furniture, fifteen restaurants, twenty-nine cafes and seventeen billiards parlors.”
While the more elegant restaurants were open on the arcade level to those with the money to afford good food and wine, the basement of the Palais Royal offered cafés with cheap drinks, food and entertainment for the masses, such as at the Café des Aveugles.

Upon the death of the duc, the palace’s ownership reverted to the state, and for a time it was known as Palais du Tribunat. After the Bourbon restoration to power in 1814, the duc d’Orléans took back his title and the Palais Royal took back its name, but kept its reputation for a fashionable meeting place. And that is when Lady Chance is set.
In 1814, Paris was under occupation by the allied forces that had defeated Napoleon. Russian cuirassiers, Prussian lancers, Hungarian hussars, Cossacks, and French soldiers all rubbed shoulders—and were not always in harmony with each other. But it was said of the Palais Royal that “You can see everything, hear everything, know everyone who wants to be found.”

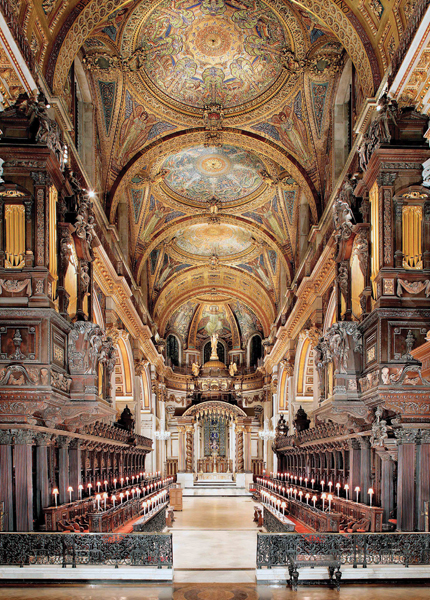
Véry Frères in the Palais Royal was accounted the most expensive restaurant in Paris, and one could dine with “brilliantly lit salons, granite tables, gilt bronze candelabra and mirror-lined walls.” Trois Frères Provençaux was famous for poulet à la Marengo—Chicken Marengo, said to be the dish served Napoleon’s victory at Marengo. In Paris Between Empires, Philip Mansel talks of dining at Le Caveau, or at the royalist Café de Foy. While Café des Mille Colonnes on the first floor of arcade provided its patrons, “Mirrored salons, hung with ‘magnificent chandeliers’ and supported by Corinthian columns of green marble.” The building was also home to the fashionable resturant Le Grand Véfour.
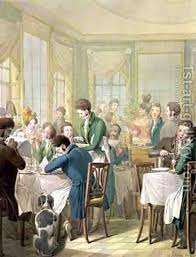
On the second floor, elegant card rooms offered deep gaming—these are the salons featured in Lady Chance.
About Lady Chance
Can an English lady find love and common ground with a French soldier?
In Paris of 1814, as Bourbon king again takes the throne, and the Black Cabinet—a shadowy group of agents employed by the British—is sent to unmask dangerous men and stop assassinations. When Diana, Lady Chauncey—known as Lady Chance—is recruited by her cousin to use her skill at cards to help him delve into these plots, she meets up with a man she thought dead. Diana finds herself swept into adventure and intrigue, and once again into the arms of the French officer she tangled with ten years ago. But she is no longer an impulsive girl, and he may not be the man she once thought was honorable and good.
After the recent defeat of his country, Giles Taliaris wants nothing more than a return to his family’s vineyards in Burgundy. But his younger brother seems involved in dangerous plots to return France to a republic. To get his family through these troubles, Giles can only tread warily. When he again meets meet the English girl he once knew and thought lost to him, he finds himself torn between duty and desire. Can he find his way through this tangle—and if he does, how can he convince his Diana to give up everything for him?
Amazon
Excerpt
Diana blinked twice and let her stare travel the room once more. “I rather thought the gaming rooms of the Palais Royal would be more…”
“Degenerate? Depraved? Decayed?” Jules asked.
“Grand, actually. Oh, the colonnade outside is charming, but this…” She fluttered a kid glove at their surroundings—at the draped windows, the high vaulted room with its plaster ceiling, the discreet décor with respectable landscapes hung over a tasteful, floral wallpaper. Chandeliers glittered overhead. Around them, dozens of uniformed gentlemen lounged or indulged in intense card play or watched the gaming with elegant women on their arms.
 She had seen Russian Cossacks in the streets, distinct with their heavy boots, loose black trousers and red jackets. Inside this room, above the closed shops of the Palais Royal, officers from the Army of Silesia leaned against the walls, their uniforms as precise as their actions. Sullen French officers lurked at the edges of the room, unhappy with the foreign soldiers who had so recently beaten them. Accents and languages tumbled around her—a hint of Dutch, a dash of French, guttural Germanic phrases. Perfumes and a hint of smoky tallow from the candles scented the air. Diana gave Jules a sideways glance. “This almost looks more like the engravings I’ve seen of London clubs.”
She had seen Russian Cossacks in the streets, distinct with their heavy boots, loose black trousers and red jackets. Inside this room, above the closed shops of the Palais Royal, officers from the Army of Silesia leaned against the walls, their uniforms as precise as their actions. Sullen French officers lurked at the edges of the room, unhappy with the foreign soldiers who had so recently beaten them. Accents and languages tumbled around her—a hint of Dutch, a dash of French, guttural Germanic phrases. Perfumes and a hint of smoky tallow from the candles scented the air. Diana gave Jules a sideways glance. “This almost looks more like the engravings I’ve seen of London clubs.”
Or like affairs of the London season, she thought. She’d had only two seasons and had not wanted a third. The play in London had always been dull or had been filled with women whose eyes glittered too brightly and gentlemen who bet too rashly. Here in the Palais Royal, just as with any notable event in London, music drifted through the rooms. A quartet was playing, she thought. Skilled enough to take on Mozart’s music and do the lively tune some justice.
Turning to her, Jules leaned closer. “The Bourbons may be back on the throne, but the Parisians look to good English coin to return prosperity. Hence this emulation of London with the rather French addition of the demi-monde in attendance. However, do not mistake matters. There are those who would have their emperor back.”
Stepping behind her, he helped her off with her cloak. He left that and his hat and cane with the porter. He wore his customary black coat, along with formal evening breeches, a white shirt, and a pale yellow waistcoat. He looked stark and properly British. She had worn gold to compliment his dress. A clinging silk that almost left her feeling a girl again with ruffles at her ankles and a daringly low Parisian neckline. They stepped into the club and Jules found them glasses of champagne. She walked the room beside him, watching him nod to acquaintances.
She had been to the Palais Royal during the day to visit the shops on the ground floor. Perfume could be had, along with toys, candy, gloves, waffles from stands, or portraits from struggling artists. But at night, the shops closed and the Palais Royal transformed itself. Véry Frères, the most expensive restaurant in Paris she had heard, offered brilliantly lit salons, granite tables, gilt-bronze candelabra and mirror-lined walls, as well as fabulous meals. In the basements of the Palais Royal, one could find establishments offering drink, food or entertainment such as at the Café des Aveugles, renowned for its orchestra of blind musicians.
They were blind for a reason for the galleries were where ladies of all shapes and colors and sizes offered themselves for sale.
This establishment—above the streets and the closed shops and below the rented rooms of those girls looking for customers—seemed designed to cater to patrons with money. There would be few enough Frenchmen who fit that description just now, Diana knew.
She had glimpsed the poverty on the journey to Paris.
The crossing to France had been long, taking fourteen hours to Boulogne with a fitful, unfriendly wind. The carriage ride to Paris had been even longer. And quite sad. This was not the country she knew from ten years ago. Old men, women, and thin boys populated the villages, for the young men had all gone to war. She had glimpsed far too many skinny cows and poorly worked fields. They had been cheered in some towns—the English liberators who had helped free France from an oppressive empire. In other towns, the French watched them pass with suspicion in their eyes. Not everyone welcomed back the rightful French king. And the destruction on the outskirts of Paris marked where battle had raged less than a fortnight ago. No wonder so many of these Frenchmen appeared so gloomy with defeat a sore and recent memory.
All that seemed put aside, however, in the pleasure houses of the Palais Royal. After a sip of champagne with bubbles that tickled her nose, Diana asked, “Just why am I being paraded?”
“A small introduction only. Making you a familiar face that will be welcomed when you deem to grace one of the tables.”
She eyed the women with their painted faces who clung to the officers’ arms. Very few sons of France seemed to be able to compete with the dashing foreigners. She glanced at Jules and kept her voice dry. “I can see the last of my respectability vanishing on the horizon.”
“Cousin, this is Paris. You may rub elbows with these delightful creatures who hire out their most intimate charms and still be free to dance with dukes and true ladies the next evening. The French understand these things.”
“It is good someone does. Now that I am decked out in the finest Paris has to offer, and have your grandmama’s emeralds hanging about my neck—I do hope your mother did not object to such a loan—what exactly is it that I am here to do?”
They had spent the journey to Paris discussing recent events, political situations, and the gossip of who was who in Paris. All of it a prelude to this—or so she guessed. To own the truth, she had simply wanted to enjoy going somewhere. Anywhere. Now she glanced around the room, a flutter in her stomach. What was she doing here? She wasn’t up to this sort of intrigue.
She forced a smile and lifted an eyebrow at Jules.
He gave her a small, approving nod. “You are doing all you must. You look a likely widow in need of amusement. Soon you shall find a spot at a select table. Win a bit. Lose more. After the drink has flowed and the hour grows late, I shall make a few introductions. Those gentlemen will lose heavily to you, I expect.”
She gave a small shrug. She had learned young how easy it was to lose at any game. Growing up, her older cousins—Jules included—had pounded home that lesson. They had never let her succeed at anything unless she deserved the win. And of her marriage—well, the less said there, the better, she thought. She twirled her fan. “Am I to keep their funds? Press them for something other than coins to clear their debts of honor to me?”
Jules’ smile did not falter, but Diana thought something hard appeared in his eyes. “Cousin, in cards, one never reveals one’s hand until all play is done. Let us say for now it is good to have certain pockets empty. It takes money to make mischief.”
She huffed out a breath. “Why do simple answers always sound only part of the truth? And chess is your game. You always plan at least seven moves ahead. So what are you not yet telling me?”
He patted her hand. “Enough for now, other than that I count on your shocking, unpredictable whims to keep us all on our toes.”
Diana shook her head and drained her champagne. “In chess, in Paris, or merely as a gamester?”
“You said it yourself—you must be an adventuress.”
Pulling in a breath, she pushed back her shoulders. “Yes, I did say so. Well, adventuring we go. Where do I begin? And I hope all this…this whatever is for a good cause.”
“Good may depend upon one’s views. Our view is to safeguard England’s interests. If certain rumors are true, a good man’s life may be at stake. However, Paris is rife just now with stories of everything from a dozen pretenders to the throne—the lost Bourbon prince returned from God knows where—to schemes that might bring back that dangerous fellow we were just discussing.”
“Ah, poor Louis-Charles, the dauphin.” She shook her head. “I would rather meet him than the former emperor.” A chill touched her back. She had met Bonaparte once. Seen him briefly, really. Before he had crowned himself emperor, and long before his recent surrender. At the time of her encounter he’d had another man’s wife on his arm, stolen from one of his generals. She still thought that a petty thing to do. She had also thought him short, fascinating in a way, and not much of a gentleman. He had once brought order to the French Revolution, but he had gone on to set Europe ablaze. And his command of a decade ago to arrest all the English in France had sent her running from Paris. That still rankled. She had been having such fun at the time. And if that had not happened, then she would not…
Ah, but this trip—and Jules—would give her better memories. She would focus on that.
It certainly took little effort to do as Jules bade her. He guided her to a table where gallant young gentlemen played—two French officers, an English gentleman in evening wear, and a Hungarian Hussar in a dashing uniform with excessive braid who at once offered her his seat. She played as Jules had asked, winning a little, losing a bit more. Jules had offered to stand the nonsense so she had no worries about emptying her purse. She found the play a touch tame. The Palais Royal was not living up to its reputation for vice. Given the circumstances, she only sipped at her wine and watched the cards fall with mild interest.
Jules soon introduced a fellow to her—a young Frenchman whose fair windswept hair and high shirt points spoke of his dandy ambitions. He joined the table, and Diana took up the cards. Jules gave her a nod and a direct stare, and she knew he wanted her to stop being careless.
She had barely dealt out the cards when a name came to her that she had never expected to hear again. A card tumbled from suddenly numb hands. Forcing a smile, Diana begged pardon. She finished the deal with stiff fingers and swept the room with a glance. It could not be, she thought, her heart beating too quick and her breath short and fast. He had died on a battlefield years ago. Someone must have only mentioned his name, that was all. But she had to look anyway. She had to be certain.
She scanned the faces nearest the entrance, seeking anything familiar—a profile, a glimpse of a captain’s uniform, a face that she could still recall from so long ago. And there—across the room in the foyer—he stood, far too solid to be a ghost.
About the Author
Shannon Donnelly’s writing has won numerous awards, including a nomination for Romance Writer’s of America’s RITA award, the Grand Prize in the “Minute Maid Sensational Romance Writer” contest, judged by Nora Roberts, and others. Her writing has repeatedly earned 4½ Star Top Pick reviews from Romantic Times magazine, as well as praise from Booklist and other reviewers, who note: “simply superb”…”wonderfully uplifting”….and “beautifully written.”
In addition to her Regency romances, she is the author of the Mackenzie Solomon, Demon/Warders Urban Fantasy series, Burn Baby Burn and Riding in on a Burning Tire, and the SF/Paranormal, Edge Walkers. Her work has been on the top seller list of Amazon.com and includes the historical romances, The Cardros Ruby and Paths of Desire.
She is the author of several young adult horror stories, and has also written computer games and offers editing and writing workshops. She lives in New Mexico with two horses, two donkeys, two dogs, and the one love of her life. Shannon can be found online at shannondonnelly.com, facebook.com/sdwriter, and twitter.