Romance of London: Strange Stories, Scenes And Remarkable Person of the Great Town in 3 Volumes
John Timbs
John Timbs (1801-1875), who also wrote as Horace Welby, was an English author and aficionado of antiquities. Born in Clerkenwell, London, he was apprenticed at 16 to a druggist and printer, where he soon showed great literary promise. At 19, he began to write for Monthly Magazine, and a year later he was made secretary to the magazine’s proprietor and there began his career as a writer, editor, and antiquarian.
This particular book is available at googlebooks for free in ebook form. Or you can pay for a print version.
The Championship of England*
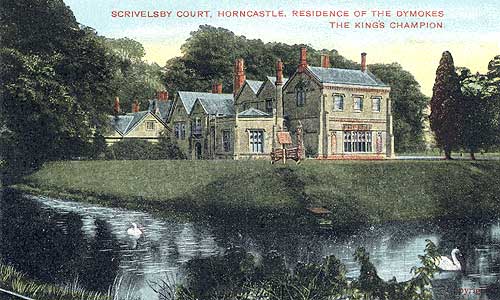
The chivalrous and dignified office of Champion of England at our coronations is conferred by the feudal manor of Scrivelsby, about two miles south of Horncastle, on the road towards Boston in Lincolnshire. By the holding of this manor, the ancient family of the Dymokes have derived the office of champion to the sovereigns of England…
The manor of Scrivesby, which was granted by the Conqueror to Robert de Marmion (Lord of Fontenoy, in Normandy), to be held by grand sergeantry, “to perform the office of champion at the King’s coronation.” The Marmians, it is said, where hereditary champions to the Dukes of Normandy prior to the conquest of England.
Sir John Dymoke served as Champion of England at the coronation of Richard II. Sir Robert Dymoke did so for Richard II, Henry VII, and Henry VIII. Sir Edward Dymoke was champion for Edward VI, Mary I, and Elizabeth I. John Dymoke was champion for George III, and when the time came for George IV’s coronation, the honor went to his grandson, Sir Henry Dymoke, due to the fact that his son, Rev. John Dymoke, was a cleric.
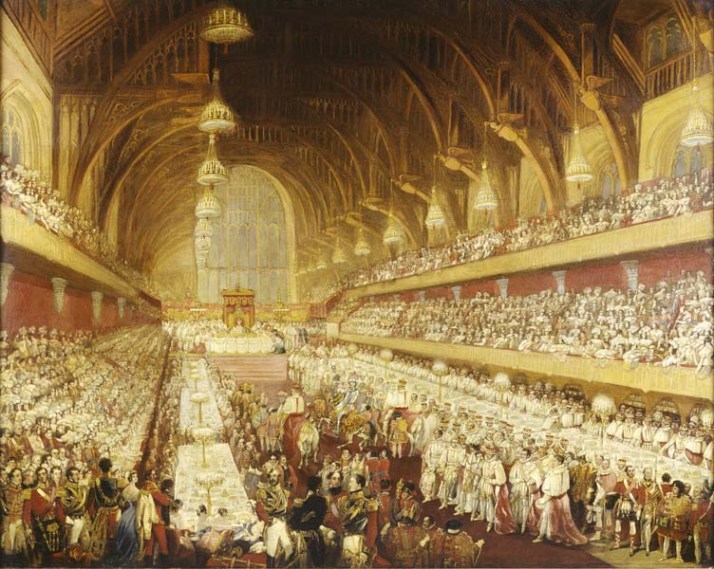

George IV’s coronation banquet was held in Westminster Hall in 1821; it was the last such banquet held.
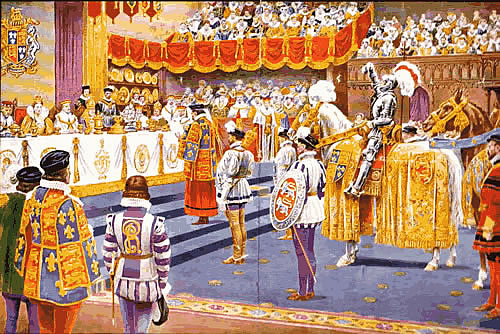
The entry of the champion at the close of the Banquet in Westminster Hall, at the coronation of George IV., was a splendid spectacle. Haydon, the historical painter, thus describes this ancient feudal ceremony which he witnessed: “The hall-doors were opened, and the flower-girls entered, strewing flowers. The distant trumpets and shouts of the people, the slow march, and at last the appearance of the King, crowned and under a golden canopy, and the universal burst of the assembly at seeing him, affected everybody… After the banquet was over, came the most imposing scene of all, the championship. Wellington, in his coronet, walked down the hall, cheered by the officers of the Guards. He shortly returned, mounted, with Lords Anglesey [formerly the Earl of Uxbridge] and Howard. They rode gracefully to the foot of the throne, and then backed out. The hall doors opened again; and outside, in twilight, a man in dark-shadowed armor appeared against the shining sky. He then moved and passed into darkness under the arch, and suddenly Wellington, Howard, and the champion stood in full view, with doors closed behind them. This was certainly the finest sight of the day. The herald then read the challenge; the glove was thrown down. They all then proceeded to the throne.”
Sir Walter Scott, in his letter describing the coronation, says, “The Duke of Wellington, with all his laurels, moved and looked deserving the baton, which was never grasped by so worthy a hand. The marquess of Anglesey showed the most exquisite grace in managing his horse, notwithstanding the want of his limb, which he left at Waterloo. I never saw so fine a bridle-hand in my life, and I am rather a judge of horsemanship. Lord Howard’s horse was worse bitted than those of the two former noblemen, but not so much as to derange the ceremony of returning back-out of the hall. The champion was performed (as of right) by young Dymoke, a fine-looking youth, but bearing, perhaps a little too much the appearance of a maiden knight to be the challenger of the world in a King’s behalf. He threw down his gauntlet, however, with becoming manhood, and showed as much horsemanship as the crowds of knights and squires around him would permit to be exhibited. On the whole, this striking part of the exhibition somewhat disappointed me, for I would have had the champion less embarrassed by his assistants, and at liberty to put his horse on the grand pas; and yet, the young Lord of Scrivelsby looked and behaved extremely well.”

The Imperial Mantle was made for the coronation of George IV in 1821 and is designed in the style of earlier ones worn by the Tudor and Stuart monarchs, it is worn over the Supertunica and the Stole. The Imperial Mantle is made of gold cloth, lined with red silk and woven with colored threads designed with a pattern of crowns, eagles, fleur-de-lis, roses, thistles and shamrock held together at the chest with a gold clasp in the form of an eagle.
*George IV’s was the last coronation to include a championship.
Romance of London Series
- Romance of London: The Lord Mayor’s Fool… and a Dessert
- Romance of London: Carlton House and the Regency
- Romance of London: The Championship at George IV’s Coronation
- Romance of London: Mrs. Cornelys at Carlisle House
- Romance of London: The Bottle Conjuror
- Romance of London: Bartholomew Fair
- Romance of London: The May Fair and the Strong Woman
- Romance of London: Nancy Dawson, the Hornpipe Dancer
- Romance of London: Milkmaids on May-Day
- Romance of London: Lord Stowell’s Love of Sight-seeing
- Romance of London: The Mermaid Hoax
- Romance of London: The Bluestocking and the Sweeps’ Holiday
- Romance of London: Comments on Hogarth’s “Industries and Idle Apprentices”
- Romance of London: The Lansdowne Family
- Romance of London: St. Margaret’s Painted Window at Westminster
- Romance of London: Montague House and the British Museum
- Romance of London: The Bursting of the South Sea Bubble
- Romance of London: The Thames Tunnel
- Romance of London: Sir William Petty and the Lansdowne Family
- Romance of London: Marlborough House and Sarah, Duchess of Marlborough
- Romance of London: The Duke of Newcastle’s Eccentricities
- Romance of London: Voltaire in London
- Romance of London: The Crossing Sweeper
- Romance of London: Nathan Mayer Rothschild’s Fear of Assassination
- Romance of London: Samuel Rogers, the Banker Poet
- Romance of London: The Eccentricities of Lord Byron
- Romance of London: A London Recluse