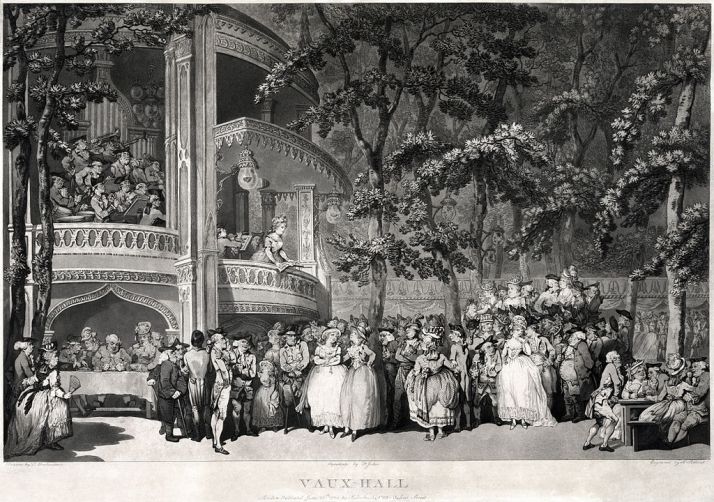
Vauxhall Gardens: A History
David Coke & Alan Borg
The Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens is one of the places I’d love to slip back in time to visit, just to catch a glimpse of what it was like. After recently splurging to buy this lovely coffee-table book, I thought it might make a wonderful subject for a new blog series. But do buy the book too, if you can! The photos are fabulous!
While the years from 1732 to 1786 were the undoubtedly the heyday of Vauxhall, the years following the Jubilee continued to attract large numbers of visitors and was the most popular outdoor entertainment for many years. Charles Burney’s daughter Sarah wrote in 1807:
You should quit your Devonshire Shades were it only to share in the universal rage there is for going to Vauxhall. I never knew anything like it. The whole London World seems to be seized with a fit of the fool.

Vauxhall Fashions, engraving (David Coke’s collection) from La Belle Assemblée no. 7 (August 1806). Many dressmakers and retailers advertised their wares as representing the latest fashions seen at Vauxhall.
Scenes from Vauxhall were presented on stage, authors such as John Keats, Pierce Egan, and William Thackeray wrote about it, and others tried to copy it, in London and elsewhere. Bath’s Sydney Gardens, opened in 1795 and much visited by Jane Austen, was modeled on Vauxhall in London, as was Tivoli in Copenhagen. Vauxhalls started appearing everywhere.
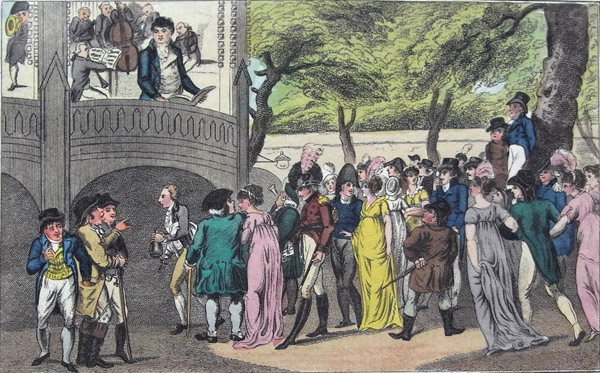
One half of the world don’t know how t’other lives, Sung by Mr. Dignum in Vauxhall Gardens, etching, 1805 (British Museum, London, 1861.0518.1087). A very popular tenor at the gardens, Dignum also gave the farewell address at the end of several seasons.
A change in clientele
In the early nineteenth century, however, with England’s middle and working classes rapidly expanding due to the Industrial Revolution and the rapid growth of London’s population, Vauxhall’s clientele began to change as well.
The social balance was changing too; the old aristocracy watched nervously as France spiralled into revolutionary chaos, and several of the great families decided to move back to the country, to avoid the potential dangers of urban unrest… In addition, social circles were becoming more restricted and inward-looking; the London aristocracy was being rapidly overtaken in terms of numbers by the professional middle classes of industrialists, businessmen, doctors and lawyers. To support them, huge numbers of labourers, tradesmen and servants moved to the capital.
Because of this influx, houses began to pop up in and around Vauxhall, which meant that the Kennington Street area was no longer a country hamlet, but a part of the city itself, and the residents didn’t always appreciate all the racket coming from Vauxhall in the early hours of the morning.

Picturesque Elevation of the Iron Bridge created over the Thames at Vauxhall, engraving, 1816 (David Coke’s collection). Designed by the engineer James Walker, the new bridge greatly shortened the land journey from London to Vauxhall Gardens.
A significant advantage was the completion of the new Vauxhall Bridge in August 1816, which shortened considerably the route from the West End.
The bridge remained open all night, both for pedestrians and for coaches, catering for those revellers who stayed on into the small hours, to the annoyance of the local residents who were trying to sleep.
A change of attractions
The form of the entertainments at Vauxhall remained traditional to the end of the eighteenth century. Various new attractions were introduced only gradually and these were directly in response to new forms of popular entertainment that had sprung up elsewhere in London.
One of these was Philip Astley’s enormously popular shows, with “daring displays of horsemanship”, as well as jugglers, tight-rope walkers, and great pageants of historical events. See my post of Astley’s Amphitheatre here.
Vauxhall had always promoted patriotic songs and military bands, and later added battle reconstructions and victory celebrations, after Astley’s model. The Battle of Waterloo was considered to be the “most spectacular event ever staged at Vauxhall.”
Boat races on the Thames was another innovation, which including a rowing race for watermen and a sailing match for ‘gentlemen’s pleasure sailing boats’. Which was followed by a grand gala in the gardens, of course. In 1812, the contest was called the Vauxhall Grand Regatta.

Vauxhall Sailing Match, engraving, 1800 (Minet Library, London, Lambeth Archives Department, V. fo. 57). This appears to be the only surviving image of one of the Vauxhall sailing matches.
Advances in science and technology brought ballooning to the gardens, the first balloon ascension beginning in 1802, but not becoming a regular feature until the 1820’s. André Jacques Garnerin, the first Vauxhall aeronaut, experimented with making parachute jumps from balloons. One of his flights included releasing a cat from a height of 600 feet, who descended safely into some resident’s garden. George Colman the younger, a playwright, wrote
Poor Puss in a grand parachute
Was sent to sail down through the air
Plump’d into a garden of fruit,
And played up old Gooseberry there:
The gardener transpiring with fear,
Stared just like a hundred struck hogs;
And swore, tho’ the sky was quite clear,
‘Twas beginning to rain cats and dogs.
Fireworks, first introduced in 1783, were limited to special occasions at first, but pyrotechnic displays did not become standard until 1798.
When it was time for the fireworks to start, a bell was rung and everyone went to the firework ground at the far eastern end of the gardens. The hours varied, displays being advertised at 9, 10 and 11 p.m.; on gala nights there was often more than one show.
Changes in proprietors and prices
Jonathan Tyers the younger’s son-in-law, Bryant Barrett, managed the gardens until his death in 1809, when his sons Jonathan Tyers Barrett and George Rogers Barrett inherited. Jonathan Barrett became sole owner in 1818. In 1821, the gardens were leased to relatives and business partners Thomas Bish and Frederick Gye, later joined by Richard Hughes, “and the trio used their option to buy the property in 1825 for £30,000.”
In 1792, the price of admission was raised to 2 shillings for regular nights and 3 shillings for the Grand Galas (masquerades), which involved elaborate fancy dress.
Susana’s Vauxhall Blog Post Series
- Vauxhall Gardens: A History
- Vauxhall Gardens: Jonathan Tyers—“The Master Builder of Delight”
- Vauxhall Gardens: A New Direction
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Orchestra and the Supper-Boxes
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Organ, the Turkish Tent, and the Rotunda
- Vauxhall Gardens: Three Piazzas of Supper-Boxes
- Vauxhall Gardens: “whither every body must go or appear a sort of Monster in polite Company”
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Competition
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Artwork, Part I
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Artwork, Part II
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Music, 1732-1859
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Business Side
- Vauxhall Gardens: Developments from 1751-1786
- Vauxhall Gardens: Thomas Rowlandson’s Painting (1785)
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Third Generation of the Tyers Family and the Jubilee of 1786
- Vauxhall Gardens: An Era of Change (11786-1822), Part I
- Vauxhall Gardens: An Era of Change (11786-1822), Part II
- Vauxhall Gardens: An Era of Change (11786-1822), Part III
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part I
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part II
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part III
- Vauxhall Gardens: The Final Years, Part IV
- Vauxhall Gardens: Farewell for ever
















