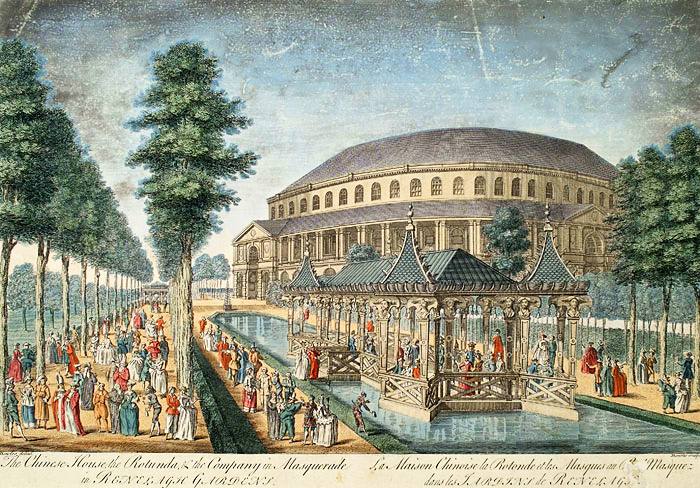
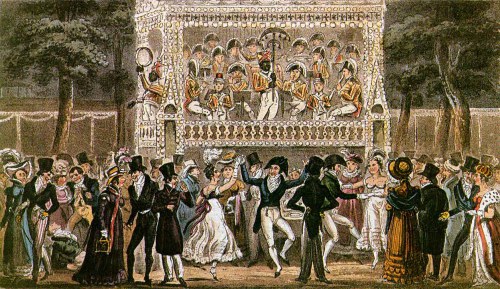Amusements of Old London
William B. Boulton, 1901
“… an attempt to survey the amusements of Londoners during a period which began… with the Restoration of King Charles the Second and ended with the accession of Her Majesty Queen Victoria.”
The Restoration and King Charles II
The puritanical opposition to everything connected with the drama… was now exchanged for the patronage of those in high places. There has perhaps never been so good a friend to the actor and to the theatrical interest generally as his Majesty King Charles. The king, by granting a patent to Mr. Tom Killigrew at the Cockpit in Drury Lane, established that principal of monopoly in things dramatic which lasted till well on in the present reign. The actors of Drury Lane were the king’s servants and a party of the royal household under the administration of the Lord Chamberlain; a certain number of them indeed wore his Majesty’s uniform of red cloth and silver lace, and ranked as Gentlemen of the Chamber. The king’s brother, the Duke of York, had his own company at the Lincoln’s Inn Theatre in Portugal Street, or at Sir Christopher Wren’s house in Dorset Gardens under Davenant, with privileges scarcely less valuable, including a patent to which theatrical historians will trace back all the subsequent glories of the great house in Covent Garden. It was under his Majesty’s auspices that women’s parts were first played by women, and he was good enough, as we know, to honour the profession by forming very intimate alliances with some of those ladies. Lastly, there has never been a more assiduous playgoer than his Majesty King Charles himself.
Relying on diarists such as Samuel Pepys and John Evelyn, Mr. Boulton states
The theatre of the Restoration was in reality much more of a social resort than the play or the opera as we know them. The pit of the playhouse of the Restoration was a social exchange, where the young man of condition displayed his graces and exchanged pleasantries with his fellows; where the man of wit discharged his carefully-prepared impromptus; and where the actors and actresses, not actually engaged on the stage, were accustomed to keep themselves in evidence by mixing freely and ostentatiously with the audience. The stage-door and the green-room, too, were attractions for a large class of men whose attentions to the actresses became a source of embarrassment to the management… Finally, the patronage which Charles the Second gave to both the theatres of his time, and the nature of his relations with some of his subjects who appeared with him in the royal box, gave an interest to a visit to the play of those days which is lacking in later and more sedate times.
Theaters of the time consisted of the pit on the ground floor, rows of continuous boxes on the first, open seats and a few boxes on the second, and the shilling gallery on the third. “The stage ran out a distance of several feet… into the body of the theatre, and was thus exposed on three of its sides to the spectators who occupied the pit.”
The prices for each sector divided the spectators into social classes. A half-crown would get you into the pit. A shilling would get an apprentice to the gallery. A box on the second floor cost eighteen pence, and the best seats in the lower section would cost about four shillings. Although you could purchase tickets for all the seats in the box for your party, if you did not, you might well find yourself sitting next to strangers.
The only manner of reserving seats in this period was to send someone ahead to pay for your ticket and hold your seat. Footmen quite frequently performed this duty for their masters and mistresses, after which they were admitted to the upper gallery to watch the play. Boulton says that “they became a very noisy, and consequently, a very important part of the audience.”
Pepys records seeing women on the stage in 1661; prior to that, women’s parts were played by men. He complains about having to spend outrageous amounts on oranges (at sixpence each) for the ladies in his company. The seats in the pit were rows of benches without backs.
I was sitting behind in a dark place, and a lady spit backward upon me by mistake, not seeing me, but after seeing her to be a very pretty lady I was not troubled at it all.
Ah, but Pepys did have a fondness for a pretty face!
He is in continual ecstasy about the beauty of one or the other of those ladies of the Court, most constant, however, to the Castlemaine, but appreciative of the Stewart, “with her little Roman nose,” or “pretty witty Nell,” or Mrs. Middleton “with a very excellent face, and body I think.” If neither Hart nor Nell nor Knipp [Mary Knep] were there the play, however good, would not please him. With Knipp present he would enjoy the worst of pieces even by the side of Mrs. Pepys. “But it is pretty to observe,” he says, “how I did look up and down and did spy Knipp, but durst not own it to my wife, who do not like my kindness to her.” Little wonder, indeed, for Mrs. Pepys surely had much to put up with. Samuel was decorum itself by her side, but when she was away he would find himself sitting in front of Knipp and Pierce, “who pulled me by the hair, so I addressed myself to them.” Knipp sang a song in the flies at the King’s House which pleased Samuel mightily, “where Knipp, after her song in the clouds, came to me in the pit.” Finally, the shameless rogue had the conscience to put on record his feelings at the performance of the “Virgin Martyr,” where “the wind musique when the angel comes down is so sweet that it ravished me, so that it made me realy sick, as I have formerly been when in love with my wife.”
Joseph Addison of The Spectator tells about the ladies of fashion in 1711 who took the notion of wearing patches on the right or left side of the forehead to indicate their adherence to a certain political party. Addison “tells us of Rosalinda, a famous Whig partisan, who had unfortunately a very beautiful mole on the Tory part of her forehead, which misled several coxcombs “to converse in the wrong strain, when on a sudden she has given them an unexpected fire which sunk them all at once.” Then there was Nigranilla too, “unhappy in a pimple, which forces her against her inclinations to patch on the Whig side.”
The Trunkmaker of the Upper Gallery
Addison’s immortal paper begins:
It has been observed that of late years there has been a certain person in the upper gallery of the playhouse, who, when he is pleased with anything on the stage, expresses his approbation by a loud knock upon the benches or the wainscot which may be heard over the whole house.
The Trunkmaker was a large black man whom nobody knew, who was never seen to smile, “but upon hearing anything to please him takes up his huge oaken plank and laid it upon the next piece of timber that stood in his way with exceeding vehemence. If the audience does not concur with him, he smites a second time, and if the audience is not yet awakened, looks round him with great wrath, and repeats the blow a third time, which never fails to produce the clap. …[H]e seldom went away from any tragedy by Shakespeare without leaving the wainscot completely shattered. The players cheerfully repair at their own cost whatever damages he makes… [T]he actors valued no applause which had not the sound of the oak plank in it.
During this time, it was common for certain fashionable braggadocios to linger on the stage and distract the audience from the play. Although Queen Anne issued a royal proclamation against it in 1711, but it was obviously not enforced, as can be seen in Mr. Hogarth’s painting of the Third Act of The Beggars’ Opera, where, in addition to the actors on the stage can be seen in the box on the right, the “Duke of Bolton ogling Vinnie Fenton, who he will presently remove from the stage and marry…” and the crowd of spectators on the stage in 1727.
As Boulton has stated, the activities of the stage were only part of the entertainment. Observing the other audience members—particularly the noble ones—was a particular interest of Samuel Pepys. A rejected swain might get his revenge by throwing rubbish at a pretty actress on the stage. A particular target for disgruntled audience was the harpsichord, but if the play or grievance was really bad, the benches and seats and other furnishings might be destroyed as well.
Opera at the King’s Theatre in Haymarket
Opera was first patronized by King George I, who “gave a subscription of £1000, as well as his own name, to the Opera House.”
Fashionable London was so fond of opera in 1735 that it paid £5000 a year to Farinelli, and when that incomparable singer was at the Haymarket an enthusiastic lady in the boxes was heard to exclaim in her ecstasy, “One God, one Farinelli.” Then singers and their competing merits were a continual joy to generations of noble patrons, and their preferences for one singer or another often inspired ladies of high fashion with very unfashionable feelings. Thus when the rival warblers Cuzzoni and Faustina were appearing at the opera in 1726, they each had a party of thick and thin supporters in distinguished circles. There was the Countess of Pembroke at the head of her party in a box, who was prepared to go all lengths for Cuzzoni; the Countess of Burlington and Lady Delaware, with their train of young men in another, were fierce and determined on behalf of the Faustina. So when Cuzzoni came on the noble faction which supported Faustina hissed her into silence, when Faustina appeared she was shrieked off the stage by the devoted band at the back of my Lady Pembroke.
By the early nineteenth century,
…there was a cult of deportment which developed in social London, and constituted a tyranny under which society groaned for a couple of generations. Beau Brummell and his set at the clubs in St. James’s Street represented the male element of this autocracy of fashion, the lady patronesses at Almack’s in King Street the feminine; and at the opera they both united their forces… There was the peerless Mr. Brummell, with his satellite exquisites in Fop’s Alley, the interest of the whole mankind of the house, we are asked to believe, centred in the question of his raiment for the evening… The ladies of the grand tier, we are told, including the chaperons, were more anxious for his notice than for that of the Prince Regent. The opera, in fact, like Almack’s, was a social function which entirely outclassed anything of the sort at Court after the retirement of the poor blind King George the Third. There was no question of getting in by the mere payment of money, a committee of ladies supervised the issue of every ticket, and a man or a lady went to the opera or did not, according as their social position was or was not considered worthy of that honour by the Lady Patronesses… who controlled London society from the time of the Regency until her Majesty came to the throne. [They] were accustomed to sit in conclave upon all the young men about to enter life, and decide as to whether or not they were eligible for admission such stately functions as Almack’s and the opera.